Lymphedema is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by the swelling of a body part, typically an arm or a leg, due to the buildup of lymph fluid. This condition occurs when the lymphatic system, which is responsible for draining excess fluid and waste products from the body's tissues, is damaged or impaired. In this article, we will delve deeper into what lymphedema is, its causes, types, symptoms, and the available treatment options.
What is the Lymphatic System?
The lymphatic system is an essential part of the immune system. It consists of a network of vessels, nodes, and organs that work together to transport lymph, a clear fluid containing infection-fighting white blood cells, throughout the body. The lymphatic system helps maintain fluid balance in the body, removes waste products from tissues, and plays a crucial role in defending against infections and diseases.
Types of Lymphedema
There are two main types of lymphedema:
Primary lymphedema: This is a rare, inherited condition in which the lymphatic system is underdeveloped or dysfunctional from birth. It can manifest at various stages in life, including infancy, puberty, or adulthood. Primary lymphedema is further classified into three subtypes based on the age of onset:
- Congenital lymphedema: Appears at birth or shortly after
- Lymphedema praecox: Develops during puberty
- Lymphedema tarda: Occurs in adulthood
- Secondary lymphedema: This is the more common form, which occurs due to damage or disruption to the lymphatic system. This damage can be caused by factors such as surgery, radiation therapy, infection, or trauma. Secondary lymphedema is often associated with cancer treatments, particularly for breast cancer, as the removal of lymph nodes or radiation therapy can lead to lymphatic system impairment.
- Symptoms of Lymphedema
Symptoms of Lymphedema
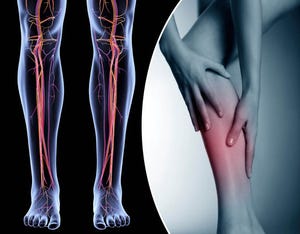
The primary symptom of lymphedema is swelling in the affected area. This swelling can vary in severity and may be accompanied by other symptoms such as:
- Heaviness or aching in the affected limb
- Restricted range of motion
- Discomfort or pain
- Recurrent infections in the affected area
- Thickening or hardening of the skin (fibrosis)
- Diagnosis and Treatment
If you suspect you have lymphedema, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis. They may use physical examination, imaging studies, and medical history to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other potential causes of swelling.
Treatment for lymphedema focuses on managing the condition and preventing complications. Common treatment options include:
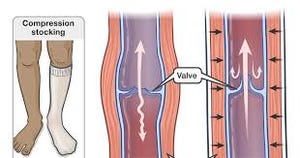
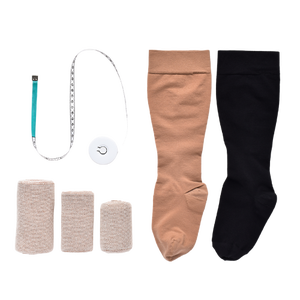
- Compression garments: These are specially designed, tight-fitting garments that apply graduated pressure to the affected area, promoting lymph flow and reducing swelling.
- Manual lymphatic drainage (MLD): This is a specialized form of massage that uses gentle, rhythmic strokes to stimulate the flow of lymph through the lymphatic system.
- Exercise: Regular, low-impact exercise can help improve lymph flow and reduce swelling. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional or a certified lymphedema therapist before starting an exercise program.
- Skin care: Proper skin care is crucial to reduce the risk of infection. This includes keeping the skin clean and moisturized, as well as promptly treating any cuts, scrapes, or insect bites.
- Complete decongestive therapy (CDT): This is a comprehensive treatment program that combines compression, MLD, exercise, and skin care. It is considered the gold standard for managing lymphedema.
- Surgical intervention: In some cases, surgery may be considered to alleviate symptoms or address underlying causes of lymphedema. Surgical options include:
- Lymphaticovenous anastomosis: This microsurgical technique connects lymphatic vessels to nearby veins, allowing lymph fluid to bypass damaged or blocked areas.
- Lymph node transfer: In this procedure, healthy lymph nodes are transplanted from another part of the body to the affected area, potentially improving lymphatic function.
- Liposuction: This may be used to remove excess fatty tissue in cases where fibrosis has occurred and non-surgical treatments have been unsuccessful.
- Living with Lymphedema
Managing lymphedema can be challenging, but with the right treatment plan and support, many individuals can lead active and fulfilling lives. Here are some tips for living with lymphedema:
- Educate yourself: Understanding lymphedema and its management is essential. Seek reliable information from reputable sources, such as healthcare professionals and support organizations.
- Seek support: Connect with others who are living with lymphedema, either in person or online, through support groups and forums. Sharing experiences and learning from others can be helpful and empowering.
- Be proactive: Take an active role in your treatment plan and work closely with your healthcare team. Communicate any concerns or changes in your condition, and follow their recommendations for self-care and treatment.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting regular exercise can help improve your overall health and may positively impact your lymphedema management.
- Be patient: It's important to remember that lymphedema management is an ongoing process, and progress may be slow. Stay committed to your treatment plan, and don't hesitate to ask for help when needed.
Lymphedema is a complex and chronic condition that requires ongoing management to reduce symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options, individuals living with lymphedema can take an active role in their care and work with healthcare professionals to develop an effective management plan. It is essential to be proactive, seek support, and maintain a healthy lifestyle to help manage lymphedema and lead a fulfilling life.