Lymphedema, a chronic condition characterized by swelling in the arms or legs, affects millions of people worldwide. While this condition is not life-threatening, it can significantly impact an individual's quality of life. Understanding the underlying causes of lymphedema can be the first step in seeking appropriate treatment and managing the condition. In this article, we will delve into the origins of lymphedema, its risk factors, and how to prevent and manage the condition effectively.
Understanding the Lymphatic System
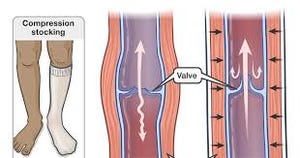
The lymphatic system is a crucial part of our immune system that helps our body fight infection and eliminate waste. It consists of lymph vessels, lymph nodes, and lymph fluid. When this system is unable to function properly, it can lead to a buildup of lymph fluid in the affected area, causing swelling and discomfort.
Primary vs. Secondary Lymphedema
Lymphedema can be classified into two categories: primary and secondary lymphedema. Primary lymphedema is a rare genetic condition resulting from the abnormal development of the lymphatic system. This type of lymphedema can be present at birth or develop during puberty or adulthood.
Secondary lymphedema, on the other hand, is more common and occurs due to damage or blockage in the lymphatic system. This damage can be caused by various factors, including:
- Surgery: Surgical removal of lymph nodes, especially during cancer treatments, can disrupt the lymphatic system, leading to lymphedema.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation used in cancer treatments can damage healthy lymphatic tissue, resulting in blockages and fluid accumulation.
- Infection: Bacterial or fungal infections can cause inflammation in the lymphatic system, obstructing the flow of lymph fluid.
- Trauma or injury: Injuries that impact the lymphatic system can lead to fluid buildup and swelling.
- Parasitic infections: Filariasis, a parasitic infection caused by roundworms, can obstruct the lymphatic system, resulting in lymphedema. This condition is more common in tropical and subtropical regions.
Risk Factors and Prevention
While lymphedema cannot always be prevented, understanding its risk factors can help in reducing its likelihood. Some risk factors associated with secondary lymphedema include:
- Obesity: Excess body weight can put pressure on the lymphatic system, impeding the flow of lymph fluid.
- Age: As we age, the risk of developing lymphedema increases due to the natural decline in the function of our lymphatic system.
- Lack of physical activity: Regular exercise is essential in promoting lymphatic flow and reducing the risk of lymphedema.
- To lower the risk of developing lymphedema, consider implementing the following strategies:
- Maintain a healthy weight: A balanced diet and regular exercise can help you maintain a healthy weight and reduce the strain on your lymphatic system.
- Practice good hygiene: Keeping the skin clean and moisturized can help prevent infections, especially in areas where lymphedema is likely to occur.
- Exercise regularly: Gentle exercises, such as swimming or walking, can stimulate the flow of lymph fluid and reduce the risk of lymphedema.
- Wear compression garments: Compression garments can help promote lymphatic flow and prevent fluid buildup.
Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with lymphedema is crucial in managing this chronic condition. While not all cases can be prevented, adopting a healthy lifestyle and following the recommended strategies can significantly lower your risk. If you suspect that you have lymphedema or are at risk of developing it, consult with your healthcare provider for further guidance and appropriate treatment options. Together, you can develop a personalized plan to manage and prevent this condition effectively.